
Do a punnett square to calculate the frequencies of the different genotypes and phenotypes for this match, and select the correct ans The gene for tall is dominant over dwarf in the garden pea plant. That other Huntington's disease gene allele can be perfectly normal, but the person still has the disease because of that one copy of the Huntington's disease gene that is mutated. Master key principles of incomplete dominance in genetics and see incomplete dominance examples in humans, animals, and plants.
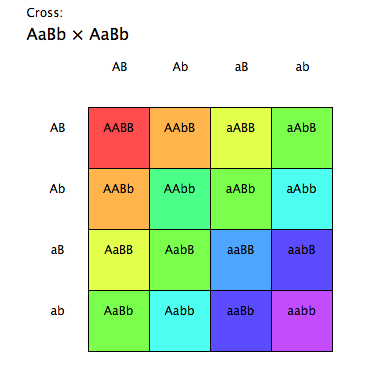
Corn is an excellent model to study Mendelian genetics as. Huntington's disease, for instance, is a dominant mutation where, if one is carrying that version of the Huntington gene, that mutation, that dominant mutation, will give the individual the disease regardless of what that person's other Huntington's disease gene allele is. The Law of Dominance refers to alternate gene forms that express the form that is dominant. Punnett squares like this one are used to visually represent how alleles are inherited and predict the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring.
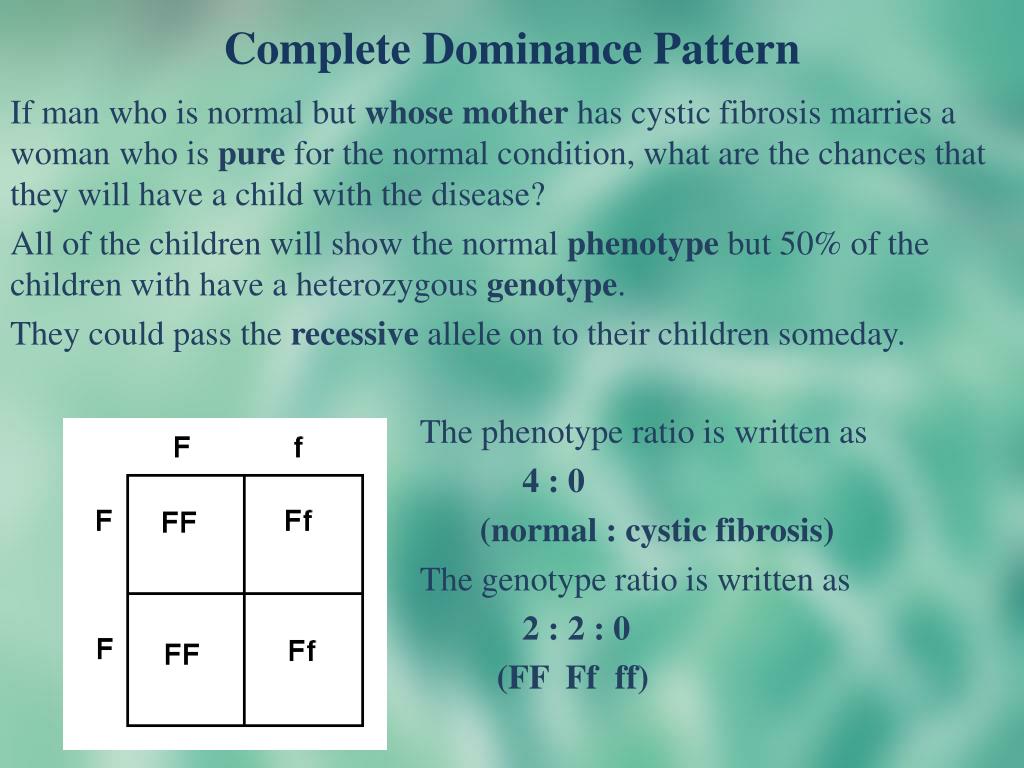
It can refer to eye color of one sort or another that can be can a dominant mutation. In that case, you're going to have a dominant mutation, and that dominant mutation can be benign. Biochemically, what is going on in this case is that the genetic variation, for a variety of reasons, can either induce a function in a cell, which is either very advantageous or very detrimental, which the other version of the gene can't cover up or compensate for. Now, it usually refers to inheritance patterns frequently used in conjunction with a Punnett square where, if an individual has two versions of a gene, and one is observed to frequently be transferred from one generation to another, then it is called dominant.

A dominant gene, or a dominant version of a gene, is a particular variant of a gene, which for a variety of reasons, expresses itself more strongly all by itself than any other version of the gene which the person is carrying, and, in this case, the recessive. This became known as Mendels Principle of Dominance, where a genotype is composed of two alleles and if the alleles differ only one phenotype will be expressed. If one is dominant, the other one must be not dominant. Dominant refers to a relationship between two versions of a gene.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
